Empathy map
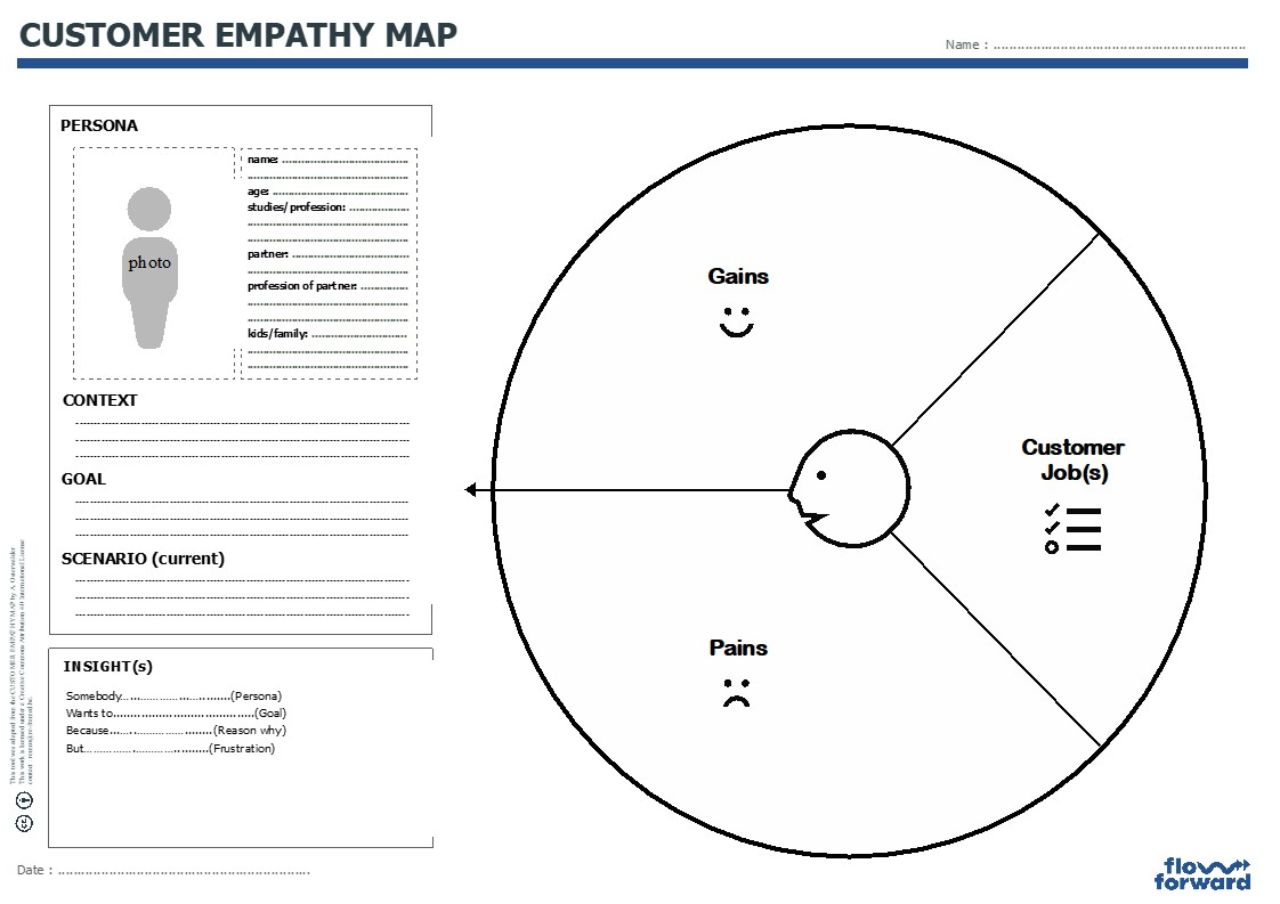
It aswers three questions :
- JOB TO BE DONE : What is the goal of the persona in the context of use?
- PAINS : What elements are impeding the persona of reaching these goals? What frustrates the user?
- GAINS What elements are helping the persona reach their goals?
The EMPATHY MAP is often combined with the VALUE PROPOSITION CANVAS, where we try to brainstorm new solutions to help our users reach their Goal with the least amount of hindrance possible.
Tips for use
Use multiple EMPATHY MAPS template to synthesize research data around your individual segmented personas. Emathy maps are best used in relatively simple projects, as the tool focuses mostly on synthesis. If the project requires analysis at greater depth, use alternative methods. Never “imagine” the content of an empathy map. Either invite Users to participate in completing the template, or –and this is the preferred approach- use the empathy map to summarize REAL qualitative research data.
How to use
EMPATHY MAPPING has 5 stages
-
Step 1 – Determine the Persona(s)
-
Step 2 – List Personas JOB TO BE DONE
-
Step 3 – List Personas customer PAINS
-
Step 4 – List Personas customer GAINS
-
Step 5 – Prioritise JOBS/PAINS/GAINS
Step 1: Determine the Persona(s)
What are the segments you wish to gather insights from? Which (extreme) user would you like to take with you in the development process?
Fill In the Persona-part of the template or (preferrably) use the more elaborate PERSONA –Template provided in the Flow Forward methodology.
-
PERSONA : Describe the person, make him/her come alive
-
CONTEXT: What is the context of use/ where will we innovate?
-
GOAL: What does the user want to achieve (current situation)
-
SCENARIO: How does the persona go about achieving these goals using products and/or services (Current context)
Step 2: List Personas JOB TO BE DONE
In essence a user is “hiring” products and services with the intent to reach goals. These goals arre called CUSTOMER JOBS, things the user wants to get done.
Jobs can be :
-
FUNCTIONAL : Perform task/solve problem (mow lawn/eat Healthy,…)
-
SOCIAL : Perception by others : trendy, professional, competent,…
-
EMOTIONAL: emotional state (feeling secure, peace of mind)
Never underestimate the social/emotional side of why people “hire” products. Think of the criteria you used to pick your latest car. Were there social (Status) or emotional (design, color) aspects involved? If you book extra travel insurance, aren’t you actually buying the emotion “peace of mind”?
Step 3: List Personas customer PAINS
Anything that impedes the user from reaching their “job to be done” is considered a pain. We make an inventory of these pains as the present us with opportunities to innovate by alleviating or even eliminating thes frustrations from the user experience.
Pains can be
-
Anything that annoys/prevents the customer from getting “the job done”
-
Undesired outcomes (functional, social or emotional)
-
Ancilliary outcomes (boring, teadious, ugly,…)
-
Obstacles preventing to even start (no time; knowledge, budget, skills…)
-
Risk (undesired POTENTIAL outcomes with negative consequences)
-
..
Step 4: List Personas customer GAINS
The user has a goal, a “job to be done”. Anything that assists the user in reaching these goals are considered CUSTOMER GAINS. These can be features of product or service, but also workarounds or other aspects that positively influence the persona’s abillity to get the job done
Gains can be
-
Required gains : minimum basic function (Nokia 3310 : it makes a call, nothing more)
-
Expected gains : Basic + added functionalities (iphone)
-
Desired gains “What if…” (phone integrated with cloud services, music libraries,...)
-
Unexpected gains : “wow a touchscreen!”
Step 5: Prioritise JOBS/PAINS/GAINS
Now you have identified the Jobs, pains and gains of your user, it is time to prioritise as not all jobs, pains and gains are equally important.